High purity crystalline silicon such as polycrystalline silicon is used to make solar panels integrated circuits and other semiconductor devices.
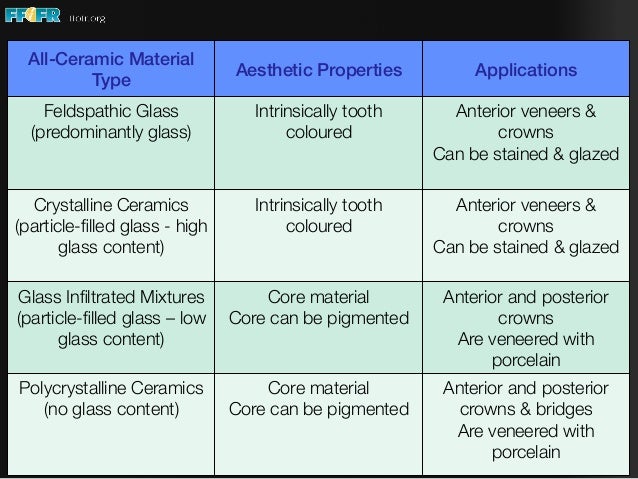
Properties of crystalline ceramics.
A hard and brittle crystalline solid and semiconductor.
There s quite a big difference between age old general purpose.
Ceramics are by definition natural or synthetic inorganic non metallic polycrystalline materials.
Usually they are metal oxides that is compounds of metallic elements and oxygen but many ceramics.
At low t s crystalline and non crystalline phases are brittle.
Polycrystalline materials are formed by multiple.
The surfaces of such materials have crystalline form or as glass an amorphous form.
We determine the above all properties with the particle sizes of the material.
Ceramic composition and properties atomic and molecular nature of ceramic materials and their resulting characteristics and performance in industrial applications.
Silicon minerals are used to make glass ceramics and are used as an aggregate in cement.
Nacl 34 801 mgo 366 2800 beo 310 2585 tic 207 3180 sic 345.
The pot is then placed on a pedestal and stands in a dish to catch the runoff during the firing.
A typical engineering stress strain curve obtained from a tensile test is shown in figure 1.
At high t s approaching tm non crystalline phases are ductile.
When the kiln reaches the maximum temperature up to 1300c.
Ceramics range from porcelain and pottery to advanced.
Industrial ceramics are commonly understood to be all industrially used materials that are inorganic nonmetallic solids.
People first started making ceramics thousands of years ago pottery glass and brick are among the oldest human invented materials and we re still designing brand new ceramic materials today things like catalytic converters for today s cars and high temperature superconductors for tomorrow s computers.
Crystalline materials have high density than non crystalline materials.
Generally ceramic particles are fine and coarse.
Ceramics are materials formed by heating and cooling.
Mechanical properties of metallic materials but many aspects also apply to nonmetals such as ceramics and glasses.
Ceramics 30 350 gpa metals 50 200 gpa polymers 50 gpa 2.
Stress strain curves when a piece of metal is subjected to a unaxial tensile force deformation of the metal occurs.
The properties of ceramics however also depend on their microstructure.
Crystalline phases are stronger.
Mechanical properties versus degree of crystallinity.
Sometimes even monocrystalline materials such as diamond and sapphire are erroneously included under the term ceramics.
It is applied very thick up to 4mm to encourage the glaze to run.