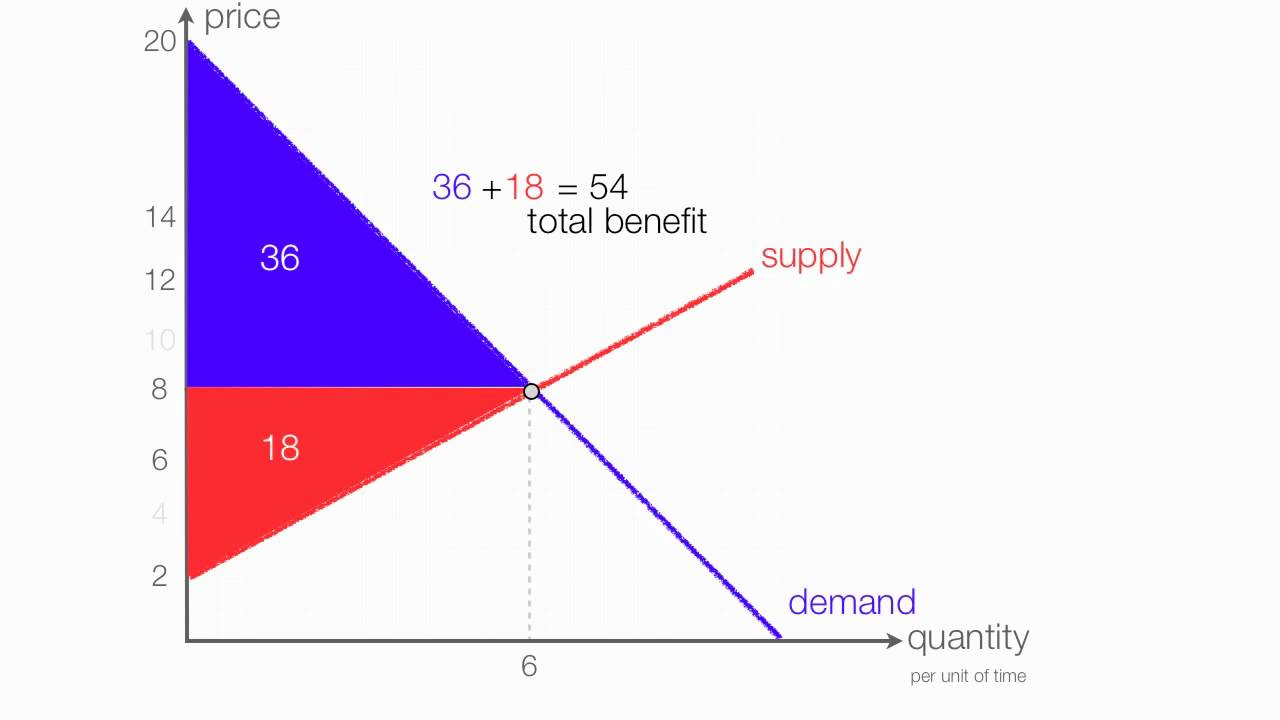
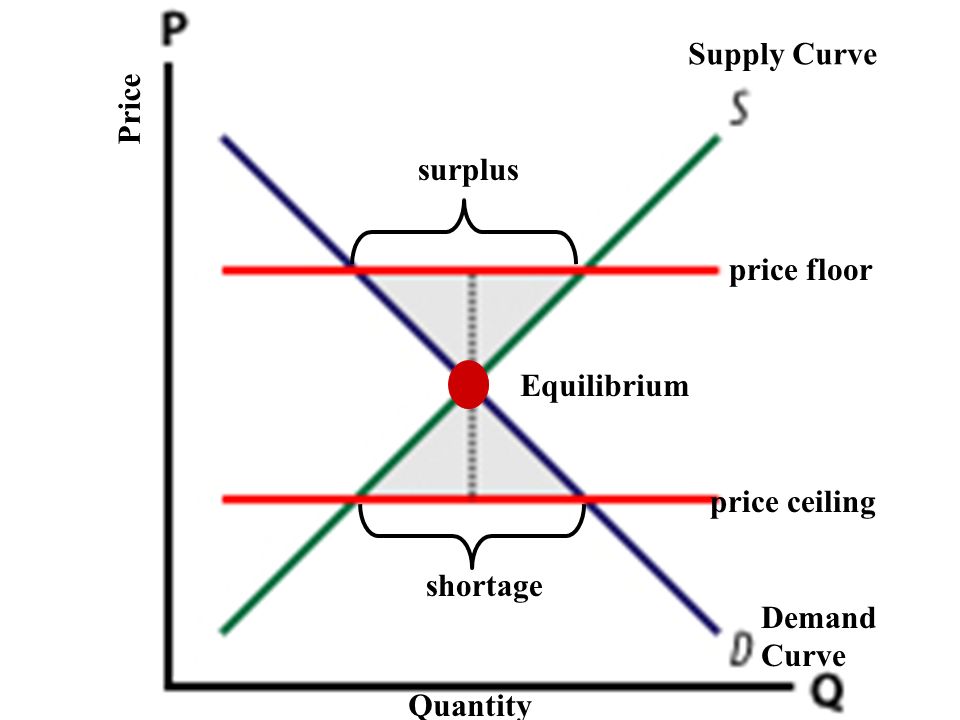
A shortage or surplus occurs when the supply for a good or service does not equal demand with shortages causing a general rise in price and surpluses causing prices to fall.
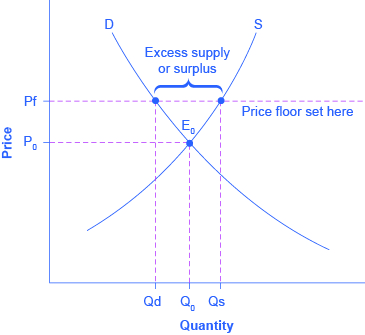
Price floor shortage or surplus.
On a graph of the supply and demand curves the supply and demand curve intersect at the equilibrium the point where the quantity.
Minimum wage and price floors.
The equilibrium price commonly called the market price is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external.
National and local governments sometimes implement price controls legal minimum or maximum prices for specific goods or services to attempt managing the economy by direct intervention price controls can be price ceilings or price floors.
In other words the market will be in equilibrium again.
A surplus or a shortage.
A price ceiling is the legal maximum price for a good or service while a price floor is the legal minimum price.
Consumers are clearly made worse off by price floors.
They are forced to pay higher prices and consume smaller quantities than they would with free market.
Any employer that pays their employees less than the specified.
Example breaking down tax incidence.
As before the equilibrium occurs at a price of 1 40 per gallon and at a quantity of 600 gallons.
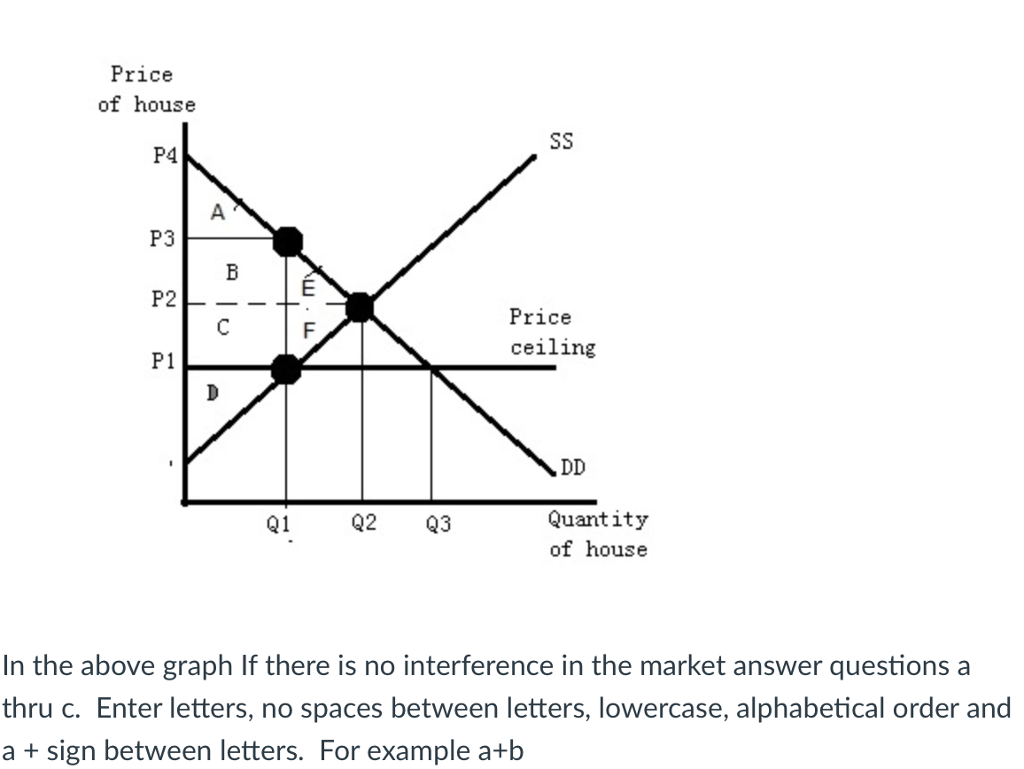
How price controls reallocate surplus.
Taxation and dead weight loss.
The price floors are established through minimum wage laws which set a lower limit for wages.
Price floors prevent a price from falling below a certain level.
Price floor is enforced with an only intention of assisting producers.
Does a binding price floor cause a surplus or shortage.
Suppliers can be worse off.
If price floor is less than market equilibrium price then it has no impact on the economy.
This is the currently selected item.
Price ceilings and price floors.
Price and quantity controls.
But the price floor p f blocks that communication between suppliers and consumers preventing them from responding to the surplus in a mutually appropriate way.
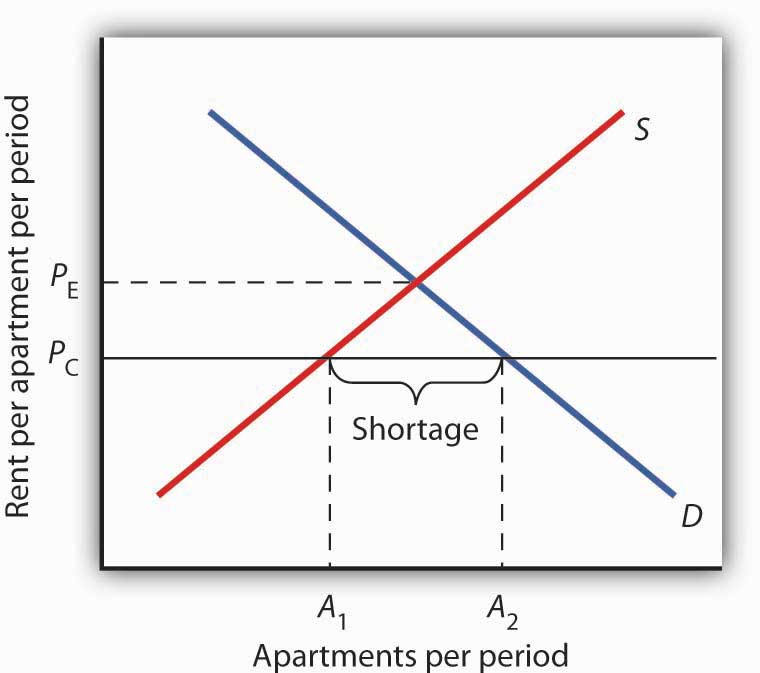
The price will rise until the shortage is eliminated and the quantity supplied equals quantity demanded.
A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective.
Price floors and price ceilings often lead to unintended consequences.
The price change continues until a new equilibrium between supply and demand is reached according to the experimental economics center from the andrew young school at.
A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service.
Surplus or excess supply.
When a price floor is set above the equilibrium price quantity supplied will exceed quantity demanded and excess supply or surpluses will result.
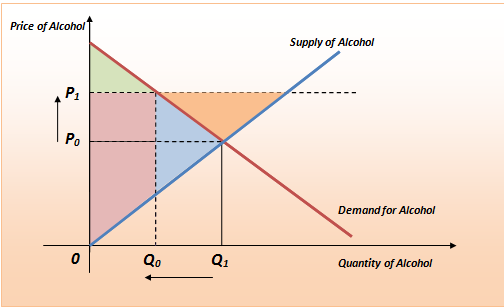
The effect of government interventions on surplus.